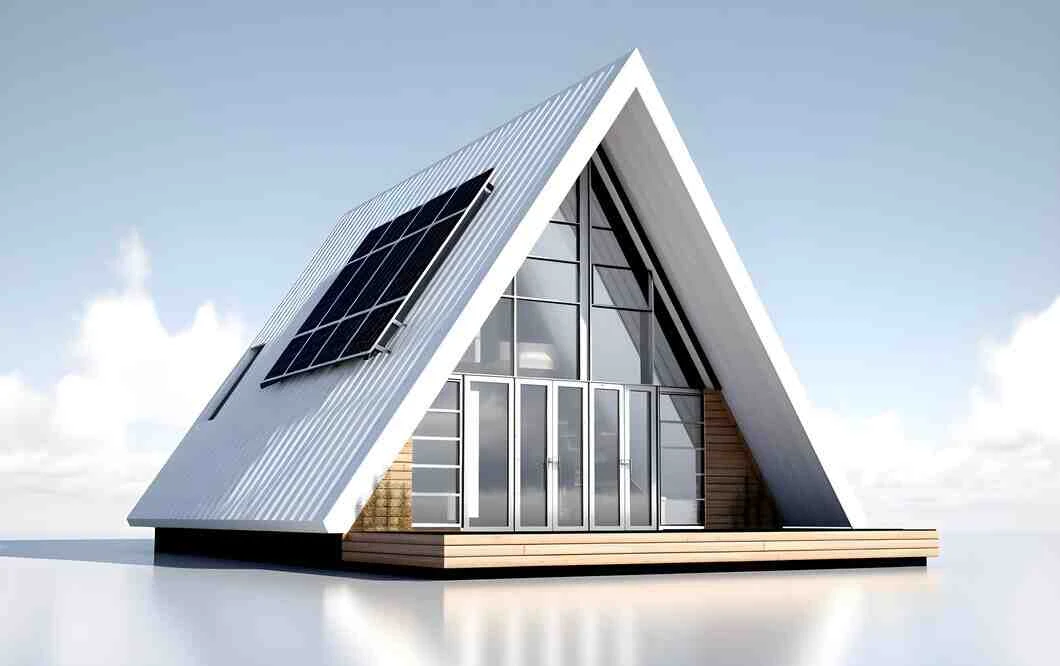
The Benefits of Sustainable Architecture: Why It Matters for Your Home
1. Energy Efficiency and Reduced Utility Costs
One of the most tangible benefits of sustainable architecture is its emphasis on energy efficiency. Sustainable homes are designed to minimize energy consumption, resulting in lower utility bills for homeowners.
1.1. Passive Solar Design: Sustainable homes often incorporate passive solar design principles, which maximize natural sunlight and minimize the need for artificial lighting and heating. This reduces electricity consumption.
1.2. High-Performance Insulation: Green homes are well-insulated to prevent heat loss in winter and maintain cool temperatures in summer. This reduces the need for heating and air conditioning, leading to substantial energy savings.
1.3. Energy-Efficient Appliances: Sustainable homes are equipped with energy-efficient appliances, further reducing electricity and water usage.
1.4. Renewable Energy Sources: Many sustainable homes incorporate renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, allowing homeowners to generate their electricity and even sell excess energy back to the grid.
2. Environmental Conservation and Reduced Carbon Footprint
Sustainable architecture places a strong emphasis on minimizing the environmental impact of construction and operation.
2.1. Reduced Resource Consumption: Green building materials are often sourced locally and chosen for their minimal environmental impact. This reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation and manufacturing.
2.2. Waste Reduction: Sustainable construction practices aim to minimize construction waste through efficient planning and recycling efforts.
2.3. Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The energy efficiency of sustainable homes translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a healthier planet.
3. Improved Indoor Air Quality
The health and well-being of occupants are central to sustainable architecture.
3.1. Low-VOC Materials: Sustainable homes use low-VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) materials and finishes, which release fewer harmful chemicals into the indoor air. This leads to improved indoor air quality and better respiratory health.
3.2. Natural Ventilation: Green homes are often designed to encourage natural ventilation, allowing fresh outdoor air to circulate and reducing the risk of indoor pollutants.
3.3. Humidity Control: Sustainable homes are equipped with humidity control systems that maintain optimal indoor humidity levels, preventing mold and mildew growth.
4. Enhanced Comfort and Quality of Life
Sustainable architecture prioritizes occupant comfort and quality of life.
4.1. Thermal Comfort: Sustainable homes are designed to maintain consistent indoor temperatures, eliminating uncomfortable drafts and temperature extremes.
4.2. Daylight and Views: Green design maximizes natural daylight and provides residents with pleasant views of the outdoors, contributing to mental well-being.
4.3. Acoustic Comfort: Sustainable homes often incorporate soundproofing measures to reduce noise pollution, creating a peaceful living environment.
5. Resilience and Future-Proofing
Sustainable architecture future-proofs homes by preparing them for environmental challenges and changes.
5.1. Climate Resilience: Green homes are designed to withstand extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and wildfires, offering increased safety and protection for occupants.
5.2. Adaptability: Sustainable homes are adaptable to changing environmental conditions, including rising temperatures and shifting weather patterns.
6. Financial Benefits
Sustainable architecture offers long-term financial advantages for homeowners.
6.1. Increased Property Value: Green homes tend to have higher property values and can command a premium in the real estate market.
6.2. Tax Incentives and Rebates: Many governments and local authorities offer tax incentives, rebates, and subsidies for sustainable home features and renewable energy systems.
6.3. Lower Maintenance Costs: Sustainable homes often require less maintenance due to their durable materials and efficient systems.
7. Connection to Nature
Sustainable architecture fosters a stronger connection between residents and the natural world.
7.1. Biophilic Design: Sustainable homes often incorporate biophilic design principles, which integrate nature into the built environment through features like indoor gardens, natural materials, and large windows that frame outdoor views.
7.2. Outdoor Living Spaces: Green homes frequently include outdoor living spaces, such as green roofs, patios, and gardens, encouraging residents to spend more time outdoors.
Conclusion
Sustainable architecture is not merely a passing trend but a transformative approach to home design that benefits homeowners, the environment, and future generations. By embracing energy efficiency, environmental conservation, improved indoor air quality, enhanced comfort, resilience, financial advantages, and a deeper connection to nature, sustainable homes offer a holistic and forward-thinking approach to living spaces. As concerns about climate change and environmental sustainability continue to grow, sustainable architecture matters more than ever, ensuring that our homes are not only spaces of comfort and shelter but also responsible contributors to a healthier planet.